What is El Niño and La Niña? Understanding These Climate Phenomena
The terms El Niño and La Niña refer to significant climate patterns that originate in the Pacific Ocean and have global weather impacts. Understanding these phenomena is crucial for predicting weather changes, preparing for natural disasters, and grasping broader climate trends. This article delves into what El Niño and La Niña are, their causes, effects, and their significance in global weather patterns.
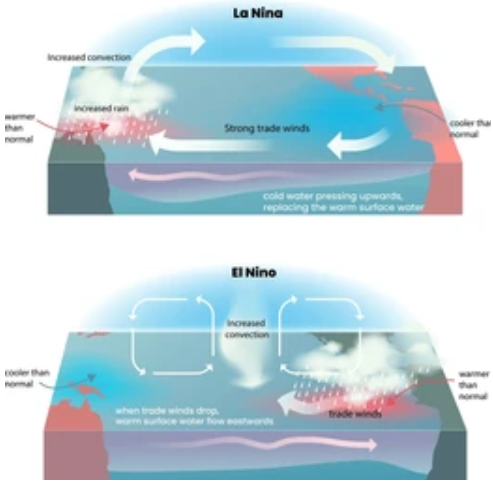
What is El Niño?
El Niño is a climate phenomenon characterized by the unusual warming of surface waters in the central and eastern equatorial Pacific Ocean. This warming disrupts typical weather patterns, leading to a variety of climatic changes globally.
Causes
El Niño occurs due to complex interactions between the ocean and the atmosphere. Key factors include:
- Weakening Trade Winds: Normally, trade winds blow from east to west across the Pacific Ocean. During El Niño, these winds weaken, causing warm water to spread eastward.
- Warm Water Movement: The shift of warm water towards the central and eastern Pacific leads to a rise in sea surface temperatures.
Effects
The impacts of El Niño are extensive and varied, including:
- Increased Rainfall: Regions like the western coast of South America often experience heavy rains and flooding.
- Droughts: Conversely, areas such as Australia and Southeast Asia may suffer from drought conditions.
- Global Temperature Rise: El Niño events typically lead to an increase in global average temperatures.
What is La Niña?
La Niña is the counterpart to El Niño, characterized by the cooling of surface waters in the central and eastern equatorial Pacific Ocean. It often follows an El_Niño event and can bring different weather patterns.
Causes
La Niña results from enhanced normal weather conditions, including:
- Strengthening Trade Winds: These winds increase, pushing warm water further west and allowing cold water to upwell in the eastern Pacific.
- Ocean-Atmosphere Interaction: The interaction between the ocean surface and the atmosphere intensifies, leading to cooler sea surface temperatures.
Effects
La Niña also has significant global impacts, such as:
- Increased Rainfall in Australia and Southeast Asia: These regions can experience more intense and frequent rains.
- Droughts in the Americas: Particularly in the southwestern United States and parts of South America.
- Temperature Fluctuations: Cooler than average temperatures in the equatorial Pacific region.
Significance and Implications
Predicting Weather Patterns
Understanding El Niño and La Niña is vital for meteorologists to predict weather patterns and prepare for extreme weather conditions. Accurate predictions can help mitigate the adverse effects on agriculture, water resources, and disaster management.
Economic Impact
These climate phenomena have profound economic implications. El Niño and La Niña can affect global markets, particularly in agriculture, fishing, and energy sectors. Preparing for these events can help reduce economic losses and enhance resilience.
Climate Change Link
Researchers are studying the relationship between El_Niño/La Niña events and long-term climate change. While these phenomena are natural, their frequency and intensity may be influenced by global warming, making ongoing research essential.
These are critical components of the Earth’s climate system, influencing weather patterns worldwide. Understanding their causes, effects, and implications can help societies better prepare for and respond to these natural events. By staying informed and proactive, we can mitigate their impacts and enhance our resilience against climate variability.

